 [Liu CHB]
[Liu CHB]|
|
Practical ecological knowledge for the temperate reader. |
Family: Ranunculaceae (Buttercup family) [E-flora]
"Perennial herb, generally glabrous. Stem: short, simple, stout, scaly. Leaf: 1–2-ternate or -pinnate, basal, petioled. Inflorescence: scapose, generally 1–4-flowered. Flower: bisexual or some staminate; sepals 5–8, petal-like, early-deciduous; petals 5–7, clawed, club-like with nectary at tip, or linear with nectary near base; pistils 4–15, short-stalked. Fruit: follicles, stalked, in umbel-like clusters, glabrous, walls papery, ± translucent. Seed: tan to dark brown, shiny, generally appearing wrinkled.
± 10 species: temperate North America, eastern Asia. (Greek: cut, from leaves) Petals sometimes considered modified staminodes." [Jepson]
 [Liu CHB]
[Liu CHB]
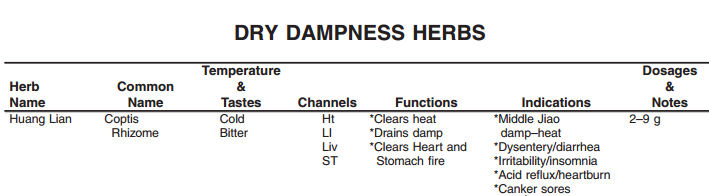
Coptis chinensis - "Synonym(s) and related species Gold thread, Mouth root, Vegetable gold. Coptis deltoidea CY Cheng et Hasio, Coptis groenlandica (Oeder) Fernald, Coptis teetoides CY Cheng, Coptis trifolia (Salis). The thread-like rhizomes contain isoquinoline alkaloids, mainly berberine and coptisine. Coptis species are used widely in Chinese medicine for infections, especially of the digestive tract, and for similar reasons as bloodroot" [HMI Stockey]
| Coptis spp. | |||
|
"...or other berberine-containing species of the same genus (WHO), which would include India’s Coptis teeta Wall., and our American Coptis trifolia (L.) Salisb." [HMH Duke] |
||
| Activities | |||
|
|
|
|
| Select Indications: Alcoholism (f; FAD; FEL); Alzheimer’s (1; COX; FNF); Arthrosis (1; COX; DAA; FNF; WHO); Boil (1; DAA; WHO); Cancer (1; COX; DAA; FNF; JLH); Cancer, gland (1; COX; JLH); Cancer, nose (1; COX; JLH); Cancer, pharynx (1; COX; JLH); Cancer, stomach (1; COX; JLH; MIC); Cancer, thyroid (1; COX; JLH); Candida (1; FAD; X2079677); Canker (1; DAA; DEM); Cold (f; DEM; FAY); Conjunctivosis (1; DAA; FAD; WHO); Cramp (f; DAA; DEM; FAD); Dermatosis (1; DAA; WHO); Diabetes (1; DAA; WHO); Diarrhea (1; DEM; MIC; WHO); Dysentery (1; DAA; WHO); Dyspepsia (f; DEM; FAD; FEL); Enterosis (1; DAA; WHO); Gastrosis (1; DEM; FAD; FEL; WHO); Infection (1; DAA; DEM); Inflammation (1; COX; DAA; FAD; FEL; FNF); Jaundice (f; DEM; FAD); Leukemia (f; JLH); Malaria (f; SKJ; WOI); Nausea (f; DAA; DEM; FAD); Pain (1; DAA; DEM); Sore (f; DAA; DEM); Sore Throat (1; DEM; FAD); Stomatosis (f; DEM; FEL); Toothache (1; DAA; WHO);Yeast (1; FAD; X2079677). [HMH Duke] | |||
| "Dosages (Goldthread) - 0.5–1.2 g powdered rhizome; 2–4 ml liquid extract (PNC); 1.5–6 g crude drug/day (WHO)." [HMH Duke] | |||
| Hazards: "Emmenagogue/uterine stimulant (AHP)....Berberine is reportedly mutagenic in yeast cells and Ames test (intercalation into the DNA). Not for use during pregnancy (PH2). If Barney is right in saying that “goldenseal should not be taken for long periods of time,” I suspect that the same would be true for those herbs containing similar compounds like barberry, goldthread, oregon grape, and yellowroot. Therefore, I lowered their safety ratings to 1 + (Barney, 1996). Coptis said to be as effective as, or more so than, sulfonamides at curing the following: acute extraocular inflammation, bacillary dysentery, diphtheria, eczema, enterosis, pertussis, pulmonary tuberculosis, purulent otitis media, surgical pyrogenic infections, and trichomoniasis vaginalis (DAA). Also said to be the best source of the COX-2 inhibitor, berberine (COX; FNF)." [HMH Duke] | |||
References
"General: Perennial herb from a yellow to pale brown rhizome; stems erect, 8-12 cm tall in flower, to 35 cm tall in fruit, smooth." [IFBC-E-flora]
"Leaves: Evergreen, all basal, stalked, 4-17 cm long, 2- or 3-times pinnately compound, occasionally twice 3-parted, the 5 or more leaflets short- to long-stalked, 2-6 cm long, egg-shaped, deeply lobed or incised, toothed." [IFBC-E-flora]
"Flowers: Inflorescence a 2- or 3-flowered cyme, the flowers nodding; bracts minute; flower stalks 1-4 cm long; petals 5-7, shorter than sepals, clawed, linear-lanceolate, bent back, flattened, nectary on inside surface near base; sepals 5-7, pale greenish-white, bent back and ascending, linear-lanceolate, 6-15 mm long, 0.3-1 mm wide; stamens 9-15." [IFBC-E-flora]
"Fruits: Follicles, 6 to 10, oblong, 7-10 mm long, spreading on stalks equal to or longer than fruit; beaks curved back, less than 1 mm long; seeds dark, ellipsoid, shiny, about 2 mm long." [IFBC-E-flora]
"Habitat / Range Moist to wet forests and bogs in the lowland and montane zones; common W of the Coast-Cascade Mountains in BC; N to SW AK and S to N WA." [IFBC-E-flora]
"Ecological Indicator Information A shade-tolerant/intolerant, submontane to subalpine, Pacific North American forb. Occurs in hypermaritime to maritime subalpine boreal and cool mesothermal climates on fresh to very moist, nitrogenpoor soils; its occurrence decreases with increasing continentality. Scattered in open-canopy coniferous forests on gleysolic or organic soils on water-receiving sites. Oxylophytic species characteristic of Mor humus forms." (Information applies to coastal locations only) [IPBC-E-flora]
Status: Native [E-flora]
References
"Coptis trifolia is an evergreen Perennial growing to 0.2 m (0ft 8in) by 0.5 m (1ft 8in). It is hardy to zone (UK) 2. It is in leaf 12-Jan It is in flower in May. The flowers are hermaphrodite (have both male and female organs)
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils. Suitable pH: acid soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland). It prefers moist soil." [PFAF]
"General: Perennial herb from a yellow to orange rhizome; stems erect, 3-12 cm tall, not elongating in fruit, minutely-hairy above." [IFBC-E-flora]
"Leaves: Evergreen, all basal, stalked, 2-11 cm long, 3-parted, the leaflets unstalked or short-stalked, egg-shaped, 1-2 cm long, slightly lobed, toothed, bases wedge-shaped." [IFBC-E-flora]
"Flowers: Inflorescence 1-flowered, erect; bracts minute; flower stalks 1-4 cm long; petals 5-7, half the length of sepals, club-shaped, fleshy, hollowed and with nectary near tip; sepals usually 5, whitish, spreading, oblanceolate to egg-shaped or elliptic, 4-11 mm long, 1-4 mm wide; stamens 30-60." [IFBC-E-flora]
"Fruits: Follicles, 4 to 7, spreading, elliptic, 4-8 mm long, on stalks equal to or longer than fruit; beaks straight but hooked at tip, 2-4 mm long; seeds dark, ellipsoid, 1-1.5 mm long, appearing wrinkled." [IFBC-E-flora]
"Habitat / Range Wet forests and bogs in the lowland and montane zones; frequent W of the Coast-Cascade Mountains in BC, rare eastward; amphiberingian, N to AK, E to NF, and S to ME, WV, and MN; Siberia, Japan." [E-flora]
Status: Native [E-flora]
"Ecological Indicator Information A shadeintolerant, submontane to montane, Asian and transcontinental North American forb. Occurs on very moist to wet, nitrogen-poor soils within boreal cool temperate and cool mesothermal climates. Scattered in open-canopy coniferous forests on gleysolic or organic soils on waterreceiving sites; common in nutrientpoor wetlands. Oxylophytic species characteristic of Mor humus forms." (Information applies to coastal locations only) [IPBC-E-flora]
Hazards
"Although no specific mention of toxicity has been found for this species, it belongs to a family that contains many species that are mildly toxic and so it is wise to treat this plant with some caution." [PFAF] "Health risks or side effects following the proper administration of designated therapeutic dosages are not recorded. Berberine has a mutagenic effect upon yeast cells and in the Ames test (intercalation into the DNA), although that does not necessarily mean a mutagenic effect for the drug when administered to humans.Pregnancy: Not to be used during pregnancy." [PDR]
Other Uses
Medicinal Uses
"Goldenthread is a very bitter tasting herb that was formerly highly valued and widely used in North America by the native Indians and white settlers alike, though it is little used in modern herbalism[254]." [PFAF]
"The drug as found in commerce consists mainly of long, thread-like, yellow rootlets, attached to a slender, terete rhizome, mixed with trifoliate leaves. Contains berberine and a white alkaloid resembling hydrastine. Tonic. Dose: 15 to 60 gr. (1 to 4 Gm.) in decoction." [Sayre]
Lore
(Coptis trifolia) Both the American Indians and the early settlers used the root as a remedy for sore and ulcerated mouths (Weiner) (one of the names for the plant is Mouthroot (Howes) ). The use has continued as a folk remedy into recent times – R B Browne quotes recipes from Alabama, not only for the original use, but also for sore eyes, even burns.
Pharmacology
"The dried roots, stems and leaves are antiphlogistic, highly astringent, sedative, stomachic, tonic[4, 21, 46, 61, 207, 222]." [PFAF] "The herb is a bitter tonic." [PDR]
Phytochemicals
"The plant contains the alkaloid 'berberine', which is a mild sedative[213], anti-inflammatory and antibacterial[222]." [PFAF]
Root: "Isoquinoline alkaloids (6 to 9%): including coptin, berberine" [PDR]
| Chemicals in: Coptis spp (Ranunculaceae) -- Generic Goldthread [DukePhyt] | |
|
ppm = parts per million |
Propagation
"Seed - best sown in a greenhouse as soon as it is ripe in an ericaceous compost[164]. Seal the pot in a polythene bag until germination takes place, which is usually within 1 - 6 months at 10°c[164]. Stored seed should be sown as early in the year as possible. Four weeks cold stratification may be beneficial[164]. Prick out the seedlings into individual pots when they are large enough to handle and grow on in a shady part of the greenhouse for at least their first winter. Plant them out in mid-autumn or in spring. Division in spring[200]." [PFAF]
"Requires a light moist humus-rich slightly acidic soil with a northerly aspect or light shade[1, 200]. A very ornamental plant[1]. The sub-species C. trifolia groenlandica (Syn C. groenlandica) is the form used medicinally in N. America[222]." [PFAF]
Synonyms